Ethylene
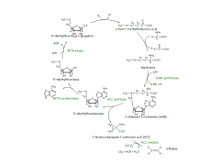
Ethylene is a gaseous hormone that has pleiotropic effects on plant development, such as leaf and flower senescence, fruit ripening, leaf abscission, and root hair growth. In Arabidopsis, seedling triple response (thickening and shortening of hypocotyl with pronounced apical hook) is a marker for ethylene action. The major ethylene biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis is shown here.
Genes on the pathway
| Gene name | Locus name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ACS1 | AT3G61510 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS2 | AT1G01480 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS3 | AT5G28360 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase like pseudo gene |
| ACS4 | AT2G22810 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS5/CIN5/ETO2 | AT5G65800 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS6 | AT4G11280 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS7 | AT4G26200 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS8 | AT4G37770 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS9/ETO3 | AT3G49700 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACS11 | AT4G08040 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase |
| ACO1 | AT2G19590 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase |
| ACO2 | AT1G62380 | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase |